Our bodies are designed to store extra calories as fat, allowing us to later burn those calories on demand if required. This process has many natural needs for us, as there were previously many times in the past we did not have regular access to food and relied upon our stored fat reserves. The reality today is far worse, however. We do not currently face times of extended lack of access to food, as modern farming and refrigeration techniques make it possible for much of the world to have access to food year round. It makes it far more difficult nowadays due to these characteristics to lose weight, and maintain a healthy weight.
Why does fat accumulate in certain areas of your body?
Where fat is deposited on our body is not at all random. Excess fat is deposited in varied areas, that depend not only on age, but gender as well. There are differences in the way genders store fat, primarily caused by the different hormones and levels of those hormones found in each. Female hormones cause fat to deposit namely around the thighs, pelvis and buttocks regions. In men, their hormones cause fat to be stored primarily around the mid section, resulting in the development of a “belly”.
Hormones do regulate how fat is stored, however, they do not change where it can be stored. Your body can only store fat where there are already fat cells, and the number of these cells you have once you become an adult will be the same number you have when you die. When you store fat, these cells expand, and when you lose weight again they will shrink back down.
Just what exactly are fat cells?
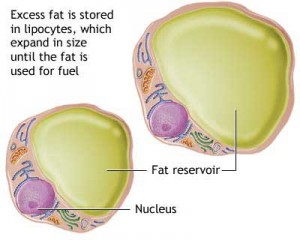 Fat cells, as the name implies, store fat and are present in our body from the moment we are born. They store lipids and complex carbohydrates for our later use for energy. Medically called adipocytes, these cells form a tissue known as adipose found over nearly every square inch of our body. Early in our lives, boys and girls have the same number of fat cells until age six. After this age, however, women tend to put on weight more quickly and have a tougher time losing weight than men do to a confluence of more fat cells in their body and hormonal impact. Research has shown that women have right around double the number of fat cells as men in adulthood.
Fat cells, as the name implies, store fat and are present in our body from the moment we are born. They store lipids and complex carbohydrates for our later use for energy. Medically called adipocytes, these cells form a tissue known as adipose found over nearly every square inch of our body. Early in our lives, boys and girls have the same number of fat cells until age six. After this age, however, women tend to put on weight more quickly and have a tougher time losing weight than men do to a confluence of more fat cells in their body and hormonal impact. Research has shown that women have right around double the number of fat cells as men in adulthood.
As noted before, after you hit a certain age you will not see any increase in number of fat cells, but your fat cells will expand when fat is deposited. This is why maintenance on the HCG diet is so critical, as the fat you lose will just come back over time without proper care and diligence about maintaining your results.
Typical areas of concern for fat deposition
It’s typical that your body will store fat all over, but any are with more fat cells will be where the major deposits of fat will fall. These include the following areas namely.
- Abdomen – Abdominal fat is stored around the mid section, and this is not gender specific. Women will develop fat in this region almost as readily as men, but men have the biggest issues with this region.
- Arms – Women store fat more readily in their arms due to lack of muscle mass in the area compared to men. Fat deposits typically occur in the tricep region, and can become a serious issue later in life.
- Thighs – Thigh fat is another area that is more prevalent for fat storage in women than men. This was always a sign of health for the development of children, and serves as excess fat stores that helped our ancestors more easily produce healthy children. Inner thighs in particular have much larger fat cell deposits in women than men.
- Buttocks – This muscle is the largest one of the body and the most important for running strength and stamina. Both men and women can store fat here, though women store it more readily in this region than men.
- Knee – The knee region may see to be an unlikely spot to store fat, but in women it’s more common and can be a problem in the long term to get rid of fat stored here. There’s no direct way to exercise this region of the body, so only diet can help.
The Good and the Bad of Fat Deposits
 The role of the fat cell is to store fat, and naturally it’s good at that job. When you store excess fat in these cells they are designed to expand and in doing so they release signals to the user’s brain to consume more food and store more fat. In this way fatty foods are often justifiably called “addictive”. This can result in a viscous cycle for the person, resulting in weight gain and obesity. Once you start trying to lose weight, your fat cells will not give up the stored fat very easily. When you burn fat, it’s often done in layers and typically isn’t done in one location over another. It’s done with all fat deposits in your body simultaneously. Many people lose weight most notably in their face and cheeks first, whenever they go on a diet plan.
The role of the fat cell is to store fat, and naturally it’s good at that job. When you store excess fat in these cells they are designed to expand and in doing so they release signals to the user’s brain to consume more food and store more fat. In this way fatty foods are often justifiably called “addictive”. This can result in a viscous cycle for the person, resulting in weight gain and obesity. Once you start trying to lose weight, your fat cells will not give up the stored fat very easily. When you burn fat, it’s often done in layers and typically isn’t done in one location over another. It’s done with all fat deposits in your body simultaneously. Many people lose weight most notably in their face and cheeks first, whenever they go on a diet plan.
How is it possible to effectively fight this process?
Once you go through this cycle a few times, gaining weight and then losing it, it can be difficult to gain motivation to try and make things better for the long term. This is understandable, and is one of the biggest consequences of obesity. What’s required to make headway in this regard is a proven weight loss treatment like the HCG weight loss program. This has been designed to combat one of the major problems of any one trying to lose weight, their hormones fighting back. This hormone helps boost the user’s metabolism and help to burn fat from key areas of the body, and does so evenly and more aggressively in areas with larger fat deposits.
HCG is a natural hormone found in pregnant women, which has been shown in studies to provide a direct link to the hypothalamus, the area of the brain responsible for appetite and metabolism. This hormone is designed to burn fat stored in the body to help with the growth of babies, however, when given without pregnancy the body will naturally burn fat more quickly and more reliably. This enables a person to go on a diet, without experiencing many of the problems with reduced weight loss over time and uneven fat loss.
